一、什么是闭包和闭包的几种写法和用法
1、什么是闭包
闭包,官方对闭包的解释是:一个拥有许多变量和绑定了这些变量的环境的表达式(通常是一个函数),因而这些变量也是该表达式的一部分。闭包的特点:
1. 作为一个函数变量的一个引用,当函数返回时,其处于激活状态。
2. 一个闭包就是当一个函数返回时,一个没有释放资源的栈区。
简单的说,Javascript允许使用内部函数—即函数定义和函数表达式位于另一个函数的函数体内。而且,这些内部函数可以访问它们所在的外部函数中声明的所有局部变量、参数和声明的其他内部函数。当其中一个这样的内部函数在包含它们的外部函数之外被调用时,就会形成闭包。
2、闭包的几种写法和用法
首先要明白,在JS中一切都是对象,函数是对象的一种。下面先来看一下闭包的5种写法,简单理解一下什么是闭包。后面会具体解释。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//第1种写法 function Circle(r) { this.r = r; } Circle.PI = 3.14159; Circle.prototype.area = function() { return Circle.PI * this.r * this.r; } var c = new Circle(1.0); alert(c.area()); |
这种写法没什么特别的,只是给函数添加一些属性。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
//第2种写法 var Circle = function() { var obj = new Object(); obj.PI = 3.14159; obj.area = function( r ) { return this.PI * r * r; } return obj; } var c = new Circle(); alert( c.area( 1.0 ) ); |
这种写法是声明一个变量,将一个函数当作值赋给变量。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
//第3种写法 var Circle = new Object(); Circle.PI = 3.14159; Circle.Area = function( r ) { return this.PI * r * r; } alert( Circle.Area( 1.0 ) ); |
这种方法最好理解,就是new 一个对象,然后给对象添加属性和方法。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
//第4种写法 var Circle={ "PI":3.14159, "area":function(r){ return this.PI * r * r; } }; alert( Circle.area(1.0) ); |
这种方法使用较多,也最为方便。var obj = {}就是声明一个空的对象。
|
1
2
3
4
|
//第5种写法 var Circle = new Function("this.PI = 3.14159;this.area = function( r ) {return r*r*this.PI;}"); alert( (new Circle()).area(1.0) ); |
说实话,这种写法我是没用过,大家可以参考一下。
总的来说,上面几种方法,第2中和第4中较为常见,大家可以根据习惯选择。
上面代码中出现了JS中常用的Prototype,那么Prototype有什么用呢?下面我们来看一下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
var dom = function(){ }; dom.Show = function(){ alert("Show Message"); }; dom.prototype.Display = function(){ alert("Property Message"); }; dom.Display(); //error dom.Show(); var d = new dom(); d.Display(); d.Show(); //error |
我们首先声明一个变量,将一个函数赋给他,因为在Javascript中每个函数都有一个Portotype属性,而对象没有。添加两个方法,分别直接添加和添加打破Prototype上面,来看下调用情况。分析结果如下:
1、不使用prototype属性定义的对象方法,是静态方法,只能直接用类名进行调用!另外,此静态方法中无法使用this变量来调用对象其他的属性!
2、使用prototype属性定义的对象方法,是非静态方法,只有在实例化后才能使用!其方法内部可以this来引用对象自身中的其他属性!
下面我们再来看一段代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
var dom = function(){ var Name = "Default"; this.Sex = "Boy"; this.success = function(){ alert("Success"); }; }; alert(dom.Name); alert(dom.Sex); |
大家先看看,会显示什么呢? 答案是两个都显示Undefined,为什么呢?这是由于在Javascript中每个function都会形成一个作用域,而这些变量声明在函数中,所以就处于这个函数的作用域中,外部是无法访问的。要想访问变量,就必须new一个实例出来。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
var html = { Name:'Object', Success:function(){ this.Say = function(){ alert("Hello,world"); }; alert("Obj Success"); } }; |
再来看看这种写法,其实这是Javascript的一个”语法糖”,这种写法相当于:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
var html = new Object(); html.Name = 'Object'; html.Success = function(){ this.Say = function(){ alert("Hello,world"); }; alert("Obj Success"); |
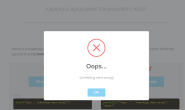
变量html是一个对象,不是函数,所以没有Prototype属性,其方法也都是公有方法,html不能被实例化。否则会出现如下错误:
但是他可以作为值赋给其它变量,如var o = html; 我们可以这样使用它:
|
1
2
|
alert(html.Name); html.Success(); |
说到这里,完了吗?细心的人会问,怎么访问Success方法中的Say方法呢?是html.Success.Say()吗?
当然不是,上面刚说过由于作用域的限制,是访问不到的。所以要用下面的方法访问:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
var s = new html.Success();s.Say(); //还可以写到外面html.Success.prototype.Show = function(){ alert("HaHa");};var s = new html.Success();s.Show(); |
二、Javascript闭包的用途
事实上,通过使用闭包,我们可以做很多事情。比如模拟面向对象的代码风格;更优雅,更简洁的表达出代码;在某些方面提升代码的执行效率。
1、匿名自执行函数
我们知道所有的变量,如果不加上var关键字,则默认的会添加到全局对象的属性上去,这样的临时变量加入全局对象有很多坏处,
比如:别的函数可能误用这些变量;造成全局对象过于庞大,影响访问速度(因为变量的取值是需要从原型链上遍历的)。
除了每次使用变量都是用var关键字外,我们在实际情况下经常遇到这样一种情况,即有的函数只需要执行一次,其内部变量无需维护,
比如UI的初始化,那么我们可以使用闭包:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
var data= { table : [], tree : {} }; (function(dm){ for(var i = 0; i < dm.table.rows; i++){ var row = dm.table.rows[i]; for(var j = 0; j < row.cells; i++){ drawCell(i, j); } } })(data); |
我们创建了一个匿名的函数,并立即执行它,由于外部无法引用它内部的变量,因此在函数执行完后会立刻释放资源,关键是不污染全局对象。
2、结果缓存
我们开发中会碰到很多情况,设想我们有一个处理过程很耗时的函数对象,每次调用都会花费很长时间,
那么我们就需要将计算出来的值存储起来,当调用这个函数的时候,首先在缓存中查找,如果找不到,则进行计算,然后更新缓存并返回值,如果找到了,直接返回查找到的值即可。闭包正是可以做到这一点,因为它不会释放外部的引用,从而函数内部的值可以得以保留。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
var CachedSearchBox = (function(){ var cache = {}, count = []; return { attachSearchBox : function(dsid){ if(dsid in cache){//如果结果在缓存中 return cache[dsid];//直接返回缓存中的对象 } var fsb = new uikit.webctrl.SearchBox(dsid);//新建 cache[dsid] = fsb;//更新缓存 if(count.length > 100){//保正缓存的大小<=100 delete cache[count.shift()]; } return fsb; }, clearSearchBox : function(dsid){ if(dsid in cache){ cache[dsid].clearSelection(); } } }; })(); CachedSearchBox.attachSearchBox("input"); |
这样我们在第二次调用的时候,就会从缓存中读取到该对象。
3、封装
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
var person = function(){ //变量作用域为函数内部,外部无法访问 var name = "default"; return { getName : function(){ return name; }, setName : function(newName){ name = newName; } } }(); print(person.name);//直接访问,结果为undefined print(person.getName()); person.setName("abruzzi"); print(person.getName()); 得到结果如下: undefined defaultabruzzi |
4、实现类和继承
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
function Person(){ var name = "default"; return { getName : function(){ return name; }, setName : function(newName){ name = newName; } } }; var p = new Person(); p.setName("Tom"); alert(p.getName()); var Jack = function(){}; //继承自Person Jack.prototype = new Person(); //添加私有方法 Jack.prototype.Say = function(){ alert("Hello,my name is Jack"); }; var j = new Jack(); j.setName("Jack"); j.Say(); alert(j.getName()); |
我们定义了Person,它就像一个类,我们new一个Person对象,访问它的方法。
下面我们定义了Jack,继承Person,并添加自己的方法。
转载请注明:苏demo的别样人生 » js闭包和闭包的几种写法及用途

 微信扫一扫,打赏作者吧~
微信扫一扫,打赏作者吧~